Home > Blog > Editing > Editing Insights
Affiliate Disclaimer: We may earn a commission if you purchase through our links
Understanding the nuances between audio polarity and phase is crucial in audio engineering and music production. These concepts, often confused, play pivotal roles in shaping sound quality. This introduction delves into their fundamental differences, setting the stage for a detailed exploration that benefits novice and seasoned audio professionals.
Audio polarity and phase, while seemingly similar, have distinct impacts on sound quality and recording. Polarity refers to the orientation of the audio signal, while phase deals with the timing of waveforms. Misalignment in either can lead to sound issues like phase cancellation, significantly affecting the overall audio output.
Continuing to read, you’ll discover practical examples of best practices in recording and mixing and learn about the software and applications that can manipulate polarity and phase. This article is a helpful resource for anyone looking to enhance their audio engineering skills or curious about these technical aspects of music production.
Table Of Contents
1. Understanding Audio Polarity And Phase
2. Differences Between Audio Polarity And Phase
3. Polarity And Phase In Recording And Mixing
4. Examples Of Polarity And Phase Manipulation
5. Software For Polarity And Phase Adjustments
6. Managing Polarity And Phase In Your Productions
7. Mastering Audio Polarity And Phase
8. FAQ

1. Understanding Audio Polarity And Phase
Audio polarity and phase concepts are critical pillars in audio engineering and music production.
These seemingly esoteric terms hold immense power in shaping the quality and integrity of sound, making their understanding essential for anyone venturing into the audio realm.
The Basics Of Audio Polarity
Audio polarity refers to the direction of a waveform relative to a defined equilibrium point. In simpler terms, it’s about whether a waveform moves up or down first.
This concept might seem trivial, but its implications are profound, especially in a recording or mixing environment. Polarity can significantly affect how sound waves interact, leading to constructive or destructive interference.
This interference, in turn, substantially impacts the clarity and quality of the sound.
Understanding Audio Phase
While polarity deals with a waveform‘s direction, phase concerns waveforms’ timing as they move through their cycle. It’s about when a sound wave begins its cycle in relation to another.
Phase issues typically arise when multiple microphones pick up the same sound source at different distances, causing the sound waves to reach each microphone at slightly different times.
When these sound waves are combined, phase cancellation can occur, leading to a hollow or flat sound.
If you want to get a deeper understanding of audio phase, here is another comprehensive article for you:
Why Polarity And Phase Matter In Music Production
Audio polarity and phase interplay are crucial in music production and sound engineering. A lack of attention to these aspects can result in recordings that lack punch, depth, or clarity.
For instance, a bass drum and guitar might cancel each other out if their waveforms are out of phase, leading to a weak low-end.
Understanding and manipulating polarity and phase allows producers and engineers to craft a more coherent, impactful, and pleasing sound.
2. Differences Between Audio Polarity And Phase
Defining Audio Polarity
Again, audio polarity refers to a sound wave’s positive or negative orientation. It’s akin to flipping a battery; reversing the polarity of an audio signal means reversing the direction of its waveform.
This can dramatically affect how different sounds interact within a mix. For example, when two identical sounds with opposite polarities are played together, they cancel each other out, resulting in silence. This phenomenon, known as phase cancellation, is crucial in audio engineering.
Exploring Audio Phase Further
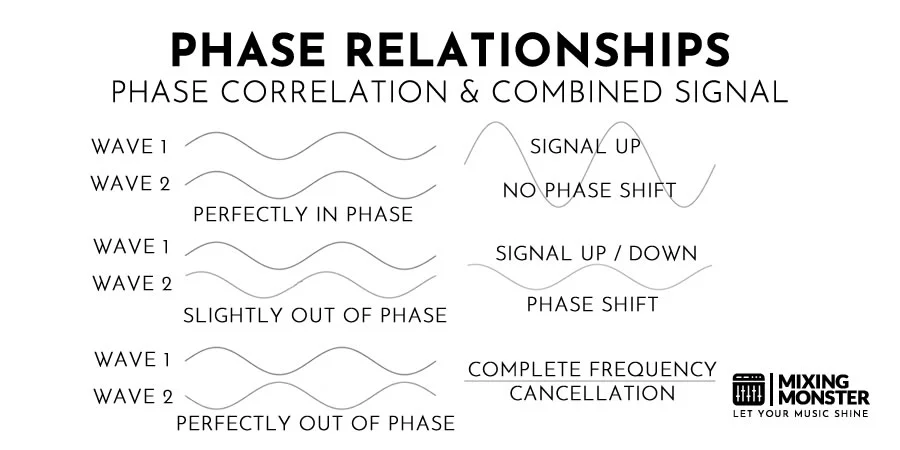
Phase, however, deals with the timing relationship between sound waves. If two waveforms are in phase, their peaks and troughs align perfectly, leading to a stronger overall sound due to constructive interference.
Conversely, when waveforms are out of phase, their peaks and troughs misalign, causing phase cancellation. This can lead to specific frequencies disappearing or the overall sound becoming thin or hollow.
Understanding phase is essential when recording with multiple microphones or mixing different sound sources.
Comparing Audio Polarity And Phase In Practice
While both concepts involve the interaction of sound waves, the critical difference lies in their nature. Polarity is a static attribute representing the direction of a waveform. Phase is dynamic, depending on the relative timing of waveforms.
In the studio, managing phase relationships is a constant challenge, especially when dealing with complex setups. Adjusting the polarity of a signal can sometimes alleviate phase issues, but it’s not a cure-all solution.
The skill lies in knowing when to change polarity or phase and how to use these adjustments creatively to enhance the audio experience.
3. Polarity And Phase In Recording And Mixing
In recording and mixing, audio polarity and phase are not just theoretical aspects; they are practical tools that can significantly influence the final sound.
The Role Of Audio Polarity In Recording
Polarity plays a vital role in recording, especially when multiple microphones are involved. For example, when recording a drum kit, the snare drum sound might be captured by both the snare mic and the overhead mics.
If the polarity between these mics is not aligned correctly, it can lead to phase issues, resulting in a thin or weak snare sound. Flipping the polarity of one mic can sometimes resolve this issue, bringing back the fullness and punch to the snare.
Audio Phase Considerations During Mixing
During mixing, phase relationships become even more critical. When combining multiple tracks, engineers must be vigilant about how the phases of different sounds interact.
This is particularly important for low-frequency sounds, where phase issues are more pronounced and can lead to losing power and definition.
Tools like phase alignment plugins and time adjustment features can help align the phases of different tracks, ensuring a coherent and powerful mix.
Techniques For Balancing Audio Polarity And Phase
Balancing polarity and phase often requires a combination of careful listening and technical know-how. It’s not just about fixing problems; it’s also about creative decision-making.
For instance, deliberately using phase cancellation can create unique sound textures, while playing with polarity can alter the spatial characteristics of a sound.
The key is to experiment and listen critically, using these tools to serve the artistic vision of the project.
4. Examples Of Polarity And Phase Manipulation
Audio Polarity Adjustment In Studio Recordings
In studio recordings, adjusting audio polarity can have a transformative effect. Consider a scenario where a drum kit and a bass guitar are recorded separately.
During mixing, the engineer notices that the kick drum and bass guitar are clashing, leading to a muddy low end. By simply flipping the polarity of the bass guitar track, the low-end frequencies suddenly snap into place, creating a more transparent and defined mix.
This simple adjustment can mean the difference between a flat, lifeless mix and one with depth and vibrancy.
Audio Phase Alignment In Live Performances
Live performance settings present unique challenges with phase alignment, especially when dealing with large PA systems and multiple microphone setups.
Sound engineers often have to make real-time adjustments to ensure that the sound projected to the audience is coherent and free from phase issues.
For example, aligning the phase of microphones used on a drum kit can prevent certain drum tones from being lost or overshadowed in the overall mix, ensuring a powerful and balanced live sound.
Interested in finding the perfect studio microphone for your audio recordings? Here you go:
Switching Audio Polarity And Phase
Switching audio polarity and phase isn’t just a corrective tool; it’s also a creative one. In the studio, engineers might experiment with these elements to create special effects or to bring a new dimension to a sound.
For example, flipping the polarity of a backing vocal track can help it sit better in the mix, making the lead vocals stand out more prominently.
Similarly, playing with the phase relationship between two guitar tracks can create a sense of width and space.

5. Software For Polarity And Phase Adjustments
In today’s digital age, various software tools in digital audio workstations (DAWs) and plugins have been developed to assist audio engineers and producers in managing audio polarity and phase.
These tools range from simple polarity switchers to sophisticated phase alignment and manipulation plugins.
Plugins For Audio Polarity Manipulation
Several high-quality plugins are designed explicitly for polarity manipulation. These plugins offer more than just a polarity inversion button; they provide detailed visual feedback and advanced controls.
For instance, some plugins allow for adjusting polarity in a frequency-specific manner, enabling engineers to flip the polarity of only specific frequency ranges.
This can be particularly useful in situations where a complete polarity inversion is too drastic or affects the overall tonality of the mix adversely.
Recommended Applications For Audio Phase Adjustment
Regarding phase adjustment, some applications offer precise control over the timing of audio signals. These tools are essential in aligning the phase of different tracks, especially when dealing with multi-microphone recordings or multi-track layering.
Some advanced applications offer automatic phase correction features, which can analyze and align tracks without manual tweaking. This can be a massive time-saver in complex mixing scenarios.
Common Software Tools For Polarity And Phase Adjustments
| Software Tool | Functionality | Best For |
| Little Labs IBP Phase Alignment Tool | Phase alignment, phase invert button | Correcting phase issues in multi-mic setups |
| Waves InPhase | Phase correction, waveform alignment | Detailed phase editing and alignment in mixes |
| Sound Radix Auto-Align | Automatic phase and time alignment | Time-saving phase correction in recording and mixing |
| Voxengo PHA-979 | Phase rotation, channel swapping | Flexible phase manipulation in stereo tracks |
| FabFilter Pro-Q 3 | Phase inversion, frequency-specific adjustment | Precise EQ and phase correction in mastering |
Integrating Polarity And Phase Tools Into Your Workflow
Integrating these tools into your audio production workflow can significantly enhance the quality of your recordings and mixes. It’s important to remember that while these tools are powerful, they are not a substitute for a good ear and sound recording practices.
They should be part of a holistic approach to sound engineering, complementing skills such as microphone placement, room acoustics understanding, and creative mixing techniques.
6. Managing Polarity And Phase In Your Productions
Navigating the intricacies of audio polarity and phase in music production requires the right tools and a set of best practices.
These practices help ensure that the final product is of the highest quality, free from unintended audio issues.
Avoiding Audio Polarity And Phase Pitfalls
One of the fundamental practices is to be proactive in preventing polarity and phase issues during the recording stage. This involves carefully placing microphones and monitoring phase relationships between different audio sources.
For instance, ensuring that microphones are equidistant from a sound source can help prevent phase issues.
Additionally, regularly checking the polarity of each track during the recording process can save a lot of time and effort in the mixing stage.
Techniques For Polarity And Phase-Optimized Sound
Listening critically for signs of phase problems, such as a lack of clarity or fullness in specific frequency ranges, is crucial during mixing.
Using tools like phase meters can help identify these issues visually. Experimenting with the positioning of tracks in the stereo field and making subtle adjustments to the timing of tracks can often resolve phase issues.
It’s also important to consider multiple tracks’ cumulative effect on the mix’s overall phase relationship.
Best Practices For Managing Audio Polarity And Phase:
- Ensure microphones are equidistant from sound sources during recording to prevent phase issues.
- Regularly check the polarity of each track to avoid conflicts and cancellations.
- Use phase meters and visual tools for identifying phase problems in mixes.
- Experiment with track positioning and timing adjustments for optimal phase alignment.
- Embrace both corrective and creative uses of polarity and phase adjustments.
7. Mastering Audio Polarity And Phase
Summarizing Audio Polarity And Phase
Understanding and mastering the concepts of audio polarity and phase is fundamental for any audio engineer or music producer.
It’s about more than just avoiding technical errors; it’s about harnessing these elements to enhance the artistic quality of the music.
Proper management of polarity and phase leads to a cleaner, more powerful, and more immersive sound, whether in a studio recording, live performance, mixing, or during the final mastering process.
The Importance Of Proper Audio Polarity And Phase
The importance of correctly handling audio polarity and phase must be balanced. They affect everything from the drums’ punchiness to the vocals’ clarity, and their mismanagement can lead to a lifeless and unengaging audio experience.
Embracing Polarity And Phase In Music Production
Embracing the complexities of polarity and phase in music production can elevate an audio engineer or producer’s work from good to great.
It requires a keen ear, a deep understanding of sound physics, and a willingness to experiment. Audio polarity and phase might seem hard to understand and manage initially, but with constant and precise practice, you get along fairly quickly!
Mastering these concepts is ongoing, with each project presenting unique challenges and opportunities to refine one’s skills.
Proper polarity and phase adjustments almost always lead to a clear, strong, and punchy sound!
8. FAQ
- What Are The Most Common Misconceptions About Audio Polarity And Phase?
Misconceptions often arise from conflating polarity and phase, thinking they are the same. Another common misunderstanding is the belief that phase issues can only be resolved during recording, ignoring the potential for correction during mixing and mastering. - How Can Incorrect Polarity Or Phase Affect The Quality Of Music Production?
Incorrect polarity or phase can lead to phase cancellation, where specific frequencies get diminished or lost, resulting in a thin, hollow, or muddy sound. This can significantly impact the audio’s clarity, depth, and power in a music production. - Are There Any Quick Tips For Identifying Polarity And Phase Issues?
Listen for signs like a lack of bass response or a hollow sound in recordings. Using phase meters and visual analysis tools can also help identify phase issues. Experimenting with polarity inversion buttons on individual tracks can be a quick way to check for improvements. - Can Phase And Polarity Be Adjusted Post-Recording?
Both can be adjusted post-recording using various digital audio workstation (DAW) tools and plugins. While it’s ideal to address these issues during recording, modern software provides significant flexibility for correction during mixing and mastering. - How Can I Switch Audio Polarity And Phase?
Switching polarity is often as simple as pressing a polarity inversion button on your DAW or mixing console. Phase adjustments involve moving tracks forward or backward in time or using specialized plugins to manipulate phase relationships between tracks.