Home > Blog > Editing > Editing Insights
In the vast universe of sound, understanding audio file formats can make a world of difference in your listening experience. From lossless formats that preserve sound in its purest form to compressed versions that save space, these digital blueprints define the quality and accessibility of audio. This guide is your definitive resource for navigating these sonic pathways with ease and confidence.
Audio file formats define how sound is digitally stored and played back. They range from uncompressed formats like WAV, which offers high quality at large sizes, to compressed formats like MP3, balancing quality and storage efficiency.
Why do some songs sound crisper while others lose details in the highs and lows? Dive into the world of audio file formats and unlock the secrets to superior sound quality that could transform your listening experience.
Table Of Contents
1. Introduction To Audio File Formats
2. The Evolution Of Audio File Formats
3. Different Types Of Audio File Formats
4. Understanding Key Audio File Formats
5. Best Audio File Formats For Mixing And Mastering
6. How To Convert Audio File Formats
7. How To Choose The Right Audio File Format
8. The Future Of Audio File Formats
9. Navigating Current Audio File Formats And Beyond
10. FAQ

1. Introduction To Audio File Formats
The Basics Of Audio File Formats
Diving into the audio world might initially seem like trying to decode an alien language. Please don’t fret; the labyrinth of audio file formats is less daunting than it appears.
At its core, an audio file format is a file structure that stores digital audio data on a computer system. Simple. This data includes crucial elements such as the sample rate, bit depth, and compression type, which jointly dictate the quality and size of the audio file.
Why Do Audio File Formats Matter?
Why should we care about audio file formats, you ask? Different audio file formats offer unique trade-offs between sound quality, file size, and system compatibility.
Understanding these trade-offs can make a significant difference if you’re a music lover, a podcast producer, a DJ, or just someone who wants to optimize your device’s storage.
From enjoying high-fidelity music to ensuring your podcast can be heard in all its glory on various platforms, the correct audio file format makes all the difference!
2. The Evolution Of Audio File Formats
Audio File Formats In The Past
Looking back, the evolution of audio file formats is an intriguing journey. The early digital age was dominated by uncompressed audio formats like AIFF and WAV, primarily due to their ability to produce high-quality sound.
However, these formats had a downside: their file sizes were gigantic. Remember trying to fit a few albums’ worths of WAV files onto a 1GB iPod? It was the equivalent of squeezing an elephant into a mini-fridge.
Overview Of Current Audio File Formats
Fast forward to the current date, the landscape of audio file formats has changed dramatically, thanks to technological advances and changes in how we consume audio. Now we have a buffet of file formats, each with strengths and weaknesses.
The ubiquitous MP3, the superior FLAC, the versatile AAC, and many more compete for space on our devices and our streaming services. But how do we know which one to pick? Explore this more detail and become a pro in selecting the proper format for your audio needs.
Stay tuned as we delve deeper into the different types of audio file formats and their specific applications in the following sections.
3. Different Types Of Audio File Formats
There are three audio file formats to consider in the dynamic world of audio. Each category provides a distinct balance between audio quality and file size. Let’s delve into each of them.
Uncompressed Audio Formats
Uncompressed audio formats, as the name suggests, store audio data without any compression. This means the audio data remains in its original, unaltered state. The result? The superior sound quality makes audiophiles rejoice! Popular uncompressed formats include WAV and AIFF.
- WAV:
High quality, large file size, widely supported - AIFF:
High-quality, large file size, created by Apple
However, the trade-off here is file size. Uncompressed audio files are akin to a feast for the ears, but they can quickly consume your device’s storage space.
Lossless Compressed Audio Formats
Enter lossless compressed audio formats, a sweet spot for many. They compress audio data to reduce file size but do so in a ‘lossless’ manner.
This means you can perfectly reconstruct the original audio data from the compressed data. Magic? Almost. FLAC and ALAC are popular lossless compressed formats.
- FLAC:
Stands for Free Lossless Audio Codec. As the name suggests, it’s free and provides lossless compression. - ALAC:
Stands for Apple Lossless Audio Codec. It’s Apple’s answer to FLAC, offering similar benefits.
Lossy Compressed Audio Formats
Last but not least, we have lossy compressed audio formats. These formats shrink file size even further but at a cost. Some audio data is permanently removed during compression.
While this data is usually outside the human hearing range, it may lead to a slight loss in audio quality. The most recognizable format in this category is MP3, but others like AAC and WMA are also popular.
Remember the challenge of fitting albums’ worth of music onto that 1GB iPod? Lossy compression came to the rescue!
We’ll zoom in on some key audio file formats in the next section. Stick around to discover their unique strengths and when to use each. Now, isn’t that music to your ears?
4. Understanding Key Audio File Formats
With a clear grasp of the different categories of audio file formats, it’s time to dive deeper. Let’s explore the unique characteristics of some critical formats, so you can master the art of choosing the right one for your needs.
.WAV: The Uncompressed Audio Standard
Think of .WAV as a giant cake full of delicious, high-quality sound. Born out of a collaboration between IBM and Microsoft, WAV is the go-to uncompressed audio format for Windows systems.
Its uncompromised sound quality makes it a favorite in professional settings, such as music production and broadcasting. But remember, with excellent quality comes great file size.
.FLAC: The Lossless Audio Powerhouse
.FLAC is the superhero of lossless compressed formats. FLAC, short for Free Lossless Audio Codec, packs high-quality audio into smaller files without losing audio information.
It’s like having your cake and eating it, too! FLAC could be your new best friend if you value quality but need to conserve storage space.
.MP3: The Universal Lossy Format
There’s a high chance you’ve already met .MP3. As the most recognized and supported audio file format, MP3 is practically universal. Thanks to its efficient lossy compression, you can store many MP3 files without much storage.
But remember, it achieves this by permanently removing some audio data. If your ears are fine-tuned to detect minute differences in sound quality, think twice about MP3.
.AAC: Apple’s Preferred Format
Enter .AAC, or Advanced Audio Coding. This lossy format is a step up from MP3 in terms of quality and efficiency, which is why it’s Apple’s format of choice for iTunes and other audio applications.
AAC is like the improved sequel to a blockbuster movie: it refines what worked with MP3. If you’re an Apple user or someone who prioritizes a balance between quality and file size, AAC could be your go-to.
This was just a glance at some key audio file formats. Next, we’ll dive into the best audio file formats for specific applications like mixing and mastering. Get ready to learn the inside secrets of the audio world. Are you all ears?

5. Best Audio File Formats For Mixing And Mastering
Are you embarking on a journey of mixing and mastering audio? Your success might hinge on the audio file formats you choose. Let’s delve into the world of audio formats and unravel the critical aspects of sample rate and bit depth that influence your audio quality.
Sample Rate And Bit Depth
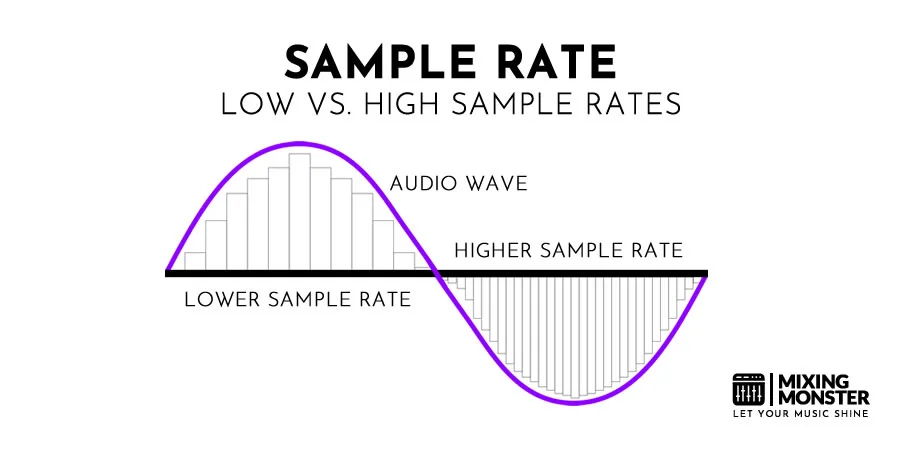
Before we dive deep into the formats, let’s understand two critical factors: sample rate and bit depth. The sample rate refers to audio recordings captured per second, typically measured in Hertz (Hz) or kilohertz (kHz). The higher the sample rate, the higher the audio quality.
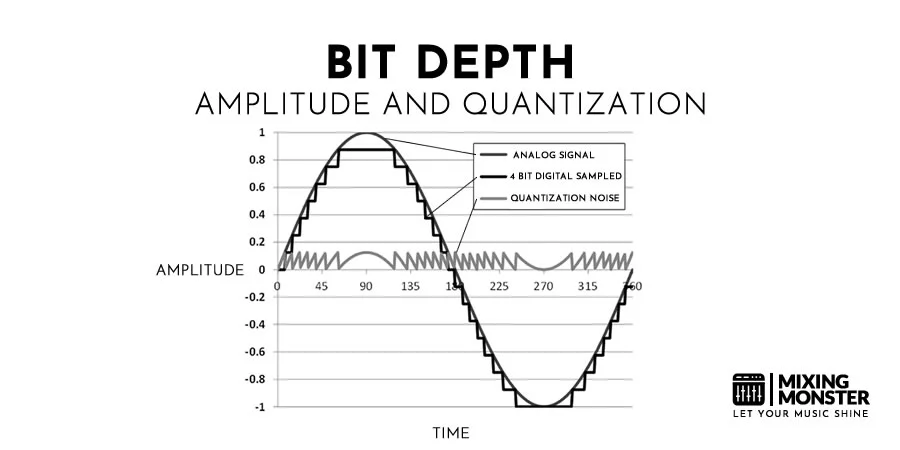
Meanwhile, bit depth pertains to the number of bits of information in each sample, impacting the audio’s dynamic range. More bits lead to better resolution of the audio signal, enhancing the sound quality.
Want to learn more about sample rate and bit depth? Here you go!
Audio Files For Mixing And Mastering
For mixing and mastering, we seek high-fidelity audio, so every nuance of the sound can be captured and manipulated. Here, uncompressed and lossless formats take center stage, providing a vast playground for audio manipulation.
Recommended Audio File Formats
Uncompressed formats like .WAV and .AIFF are prime picks for their stellar quality. Lossless compressed format.FLAC also finds a spot for its balance of quality and storage needs.
Here’s a list of the top three audio file formats for mixing and mastering, along with typical sample rates and bit depths:
-
- .WAV: Boasts stellar quality. Commonly used with a sample rate of 44.1 kHz or 48 kHz and a bit depth of 16 or 24.
- .AIFF: An Apple favorite. Like .WAV, it’s typically used with a sample rate of 44.1 kHz or 48 kHz and a bit depth of 16 or 24.
- .FLAC: For the quality-conscious, space-saving crowd. Usually used with a sample rate of 44.1 kHz and a bit depth of 16.
Choosing the proper format with the appropriate sample rate and bit depth is crucial. Your specific needs and the final destination of your audio should guide your decision.
Are you ready to dive deeper into the world of audio file formats? Next, we’ll learn the art and science of converting audio file formats. This knowledge will be helpful if you’re looking to free up storage or prep an audio file for a specific application.
6. How To Convert Audio File Formats
So, you’ve got an audio file, but it’s not in the format you need? No problem! Converting audio file formats is more effortless. This section will guide you through the conversion process and introduce some tools to simplify your job.
Audio File Conversion Software And Tools
Many software tools and online platforms can assist you in converting audio file formats. Some popular ones include Audacity, Adobe Audition, and online converters like Zamzar or Online-Convert. When selecting a tool, consider its ease of use, conversion speed, supported file formats, and output quality.
Step-By-Step Audio File Conversion Process
Let’s look at a basic step-by-step process of converting audio file formats:
- Select Your Conversion Tool:
Pick a suitable tool and install it if necessary. - Open The Audio File:
Launch the tool and open the file you wish to convert. - Choose The Output Format:
Select the format to which you want to convert your audio file. - Adjust Settings If Needed:
Some tools allow you to customize the bit rate, sample rate, or other parameters. Adjust these according to your needs. - Convert The Audio File:
Start the conversion process. Once completed, the tool should allow you to save your new audio file.
Remember, the conversion process might vary slightly depending on your chosen software or tool.
Mastering the conversion of audio file formats can open a world of possibilities for your audio projects. We’ve covered you, from assessing your audio needs to considering file size and quality.
Next, we’ll look at choosing the correct audio file format for your specific needs. Are you ready to continue our journey into audio file formats?
7. How To Choose The Right Audio File Format
Regarding audio file formats, one size does not fit all. The ideal format depends on what you want to achieve with your audio file. This section will help you navigate the sea of formats and make the best choice for your needs.
Assessing Your Audio Needs
Firstly, you need to understand your audio needs. Are you editing, storing, or streaming the audio? Are you concerned about storage space, or is audio quality your top priority?
Do you need compatibility with specific devices or software? Answering these questions will help steer you toward the correct format.
Considerations For Audio File Size And Quality
Next, consider the file size and quality trade-off. Uncompressed and lossless formats deliver superior quality but can consume considerable storage space. On the other hand, lossy formats can drastically reduce file size at the expense of some audio quality.
Here’s a quick table comparing these aspects for standard audio file formats:
| File Format | Quality | File Size |
| .WAV | Highest | Large |
| .AIFF | Highest | Large |
| .FLAC | High | Moderate |
| .MP3 | Moderate to Low | Small |
| .AAC | Moderate to Low | Small |
Choosing the suitable audio file format is like fitting a piece of a puzzle – it has to match your needs perfectly. Whether you are an audiophile, a podcast producer, or a casual listener, there’s an audio file format just right for you.
Next, we’ll explore the future of audio file formats, peeking into what’s coming next in this exciting field. Ready to leap into the future with us?
8. The Future Of Audio File Formats
In the ever-evolving world of technology, even audio file formats are still growing. The future is ripe with potential for innovations that could revolutionize the way we create, share, and consume audio.
Let’s peek into what the future might hold for audio file formats.
Emerging Trends In Audio File Formats
As audio hardware and streaming technologies improve, the demand for higher-quality audio grows, pushing these formats to the forefront. One trend is the increased use of lossless formats, like .FLAC and .ALAC, thanks to advancements in data compression and increased storage capacities.
There’s also growing interest in 3D audio formats, which offer an immersive listening experience by emulating how humans perceive sound in real life. Formats like Ambisonics and MPEG-H 3D audio are the beginning of this immersive audio revolution.
Audio File Predictions For The Future
What could be next for audio file formats? It’s challenging to say confidently, but we can make educated guesses.
We could see the development of new lossless formats, offering even higher audio quality with smaller file sizes. The future might also bring more universal formats compatible with various devices without sacrificing quality.
The world of audio is boundless and full of potential. Whether it’s higher quality, smaller sizes, or more immersive experiences, the future of audio file formats is an exciting journey.
As we move forward, we aim to keep you updated and prepared for whatever comes next in this vibrant landscape.
9. Navigating Current Audio File Formats And Beyond
With all this newfound knowledge of audio file formats, you’re well on your way to mastering the audio world. But remember, like with all technology, change is the only constant. Staying abreast of the latest trends and technologies is vital to continuing success in this field.
The Importance Of Adaptability
Being flexible and adaptable is crucial when navigating the realm of audio file formats. As new formats emerge and old ones become obsolete, you must adjust your approach accordingly.
Whether embracing lossless formats for superior audio quality or experimenting with 3D audio for immersive experiences, be open to learning and exploring new territories.
Keeping Up With Technology
Keep up with advancements in audio technologies. This could mean upgrading your audio equipment to take full advantage of higher-quality formats or learning to use new audio editing and conversion software.
And, of course, continue to educate yourself about the latest trends and developments in audio file formats.
As we conclude this comprehensive guide, remember that your journey into the audio world is beginning. With every new format, tool, or trend, there’s always something new to learn and explore.
10. FAQ
- What Is The Best Audio File Format For Quality?
The .WAV and .AIFF formats, being uncompressed, offer the highest audio quality, as they preserve all the audio data from the original recording. However, .FLAC and .ALAC are lossless formats and provide high-quality audio while taking up less storage space. - How To Convert Audio File Formats?
Audio file formats can be converted using various software tools or online platforms. The basic process involves opening the file you want to convert in the selected tool, choosing the output format, adjusting settings if needed, and initiating the conversion. - What Is The Difference Between Lossless And Lossy Audio?
Lossless audio formats, such as .FLAC and .ALAC compress audio data without losing any information, preserving the original quality. Lossy formats, such as .MP3 and .AAC, compress data by removing some audio information, resulting in smaller file sizes but potentially lower audio quality. - Are Some Audio File Formats More Universal Than Others?
Some formats like .MP3 and .AAC are more universally supported across various devices and platforms due to their balance of sound quality and file size. - What Is The Future Of Audio File Formats?
The future might see an increased use of lossless and 3D audio formats. As data compression and storage capacities improve and immersive audio experiences gain popularity, these formats are expected to become more prevalent.