Home > Blog > Editing > Editing Techniques
Affiliate Disclaimer: We may earn a commission if you purchase through our links
Audio editing is an art, and mastering how to fade audio seamlessly is a critical skill in creating perfect transitions. Whether mixing music, editing a podcast, or working on any audio project, the ability to fade audio smoothly can make a significant difference in the quality of your final product. This skill is essential for ensuring a professional and polished sound.
Fading audio, a critical technique in audio editing, involves gradually decreasing or increasing the volume to achieve smooth transitions. Essential for creating polished audio outputs, it requires precision in timing and amplitude adjustments. This technique is widely used across music production, broadcasting, and podcasting to enhance the listening experience.
Continuing to read will offer you insights into various techniques of fading audio. Whether a beginner or an experienced audio editor, you’ll find valuable tips and tricks to achieve those perfect, seamless transitions that can transform your audio projects.
Table Of Contents
1. Audio Fading Basics
2. Tools For Audio Fading
3. Techniques For Seamless Audio Fades
4. Audio Fading Mistakes And How To Avoid Them
5. Advanced Audio Fading Techniques
6. Practical Audio Fading Applications
7. Audio Fading Tips And Tricks
8. Audio Fading: Get Seamless Audio Transitions
9. FAQ

1. Audio Fading Basics
Understanding The Basics Of Audio Fading
Audio fading is an indispensable technique in sound editing and production. At its core, audio fading involves the gradual increase or decrease of sound volume, a seemingly simple process that requires skill and understanding to execute effectively.
This technique is foundational in various audio projects, from crafting a compelling music track to producing a gripping podcast episode. To master audio fading, one must grasp its basic principles. The process typically involves manipulating the sound volume at the beginning or end of a track.
Still, it can also be employed creatively in the middle of audio clips to achieve various effects. The essence of audio fading lies in its ability to subtly control the listener’s auditory experience.
By adjusting the volume, audio editors can guide the listener’s attention, create anticipation, or provide relief, thereby enhancing the overall impact of the audio piece.
Importance Of Audio Fades In Professional Editing
In professional audio editing, the role of audio fades extends beyond mere aesthetics. These fades serve multiple practical purposes: they ensure smooth transitions between tracks, help remove or mask unwanted noises, and can be used to emphasize or de-emphasize specific audio parts.
For instance, a gradual fade-out at the end of a song can provide a sense of closure, while a sharp fade-in might be used to capture the listener’s immediate attention.
The application of audio fades is a hallmark of professionalism in sound editing. A well-executed fade can seamlessly blend tracks, making the transitions almost inaudible to the listener.
Conversely, poorly executed fades can disrupt the audio flow, creating a jarring listening experience.
Thus, understanding and skillfully applying fading techniques are crucial in achieving a polished and refined audio output.
Different Types Of Audio Fades
Exploring the various types of audio fades is essential for any aspiring audio editor. Some common fade types include:
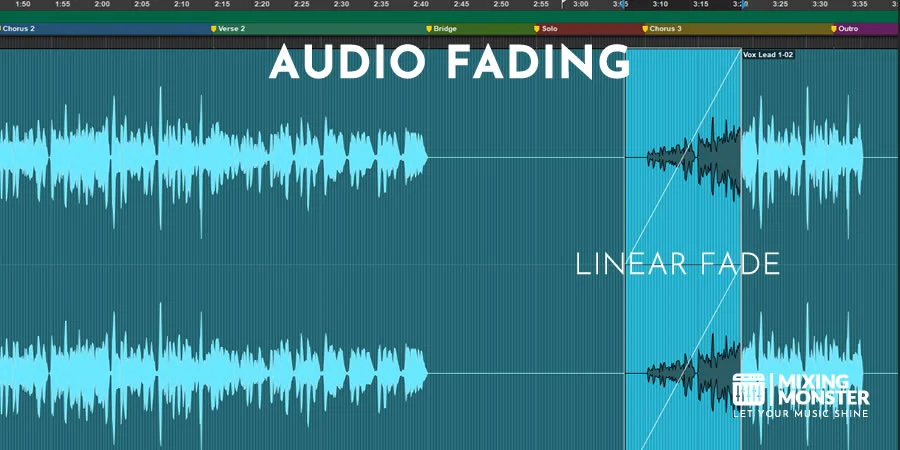
- Linear fades, where the volume change occurs constantly.
- Logarithmic fades, which feature a more gradual volume decrease.
- Exponential fades are known for their rapid volume drop-off.
Each audio fade type has its unique characteristics and use cases.
For example, linear fades are often used in musical transitions due to their straightforward and uniform nature.
Logarithmic fades are preferred in scenarios where a gentle, more natural-sounding decrease in volume is desired, such as in the background music for podcasts.
Exponential fades, with their abrupt nature, are ideal for dramatic effects or to swiftly draw attention away from a particular sound.
Selecting the appropriate fade type depends on the specific needs of the audio project. Factors like the genre of music, the mood of the podcast, or the dynamics of a film scene can influence which fade type is most suitable.
Here is a list of common audio fade types:
| Fade Type | Characteristics | Common Usage |
| Linear Fade | Volume decreases at a constant rate | Uniform transitions in songs, background music |
| Logarithmic Fade | Gradual decrease in volume, more natural ending | Natural sound endings, podcast background music |
| Exponential Fade | Rapid decrease in volume, more abrupt | Dramatic effects and quick transitions in audio tracks |
| S-Curve Fade | Starts and ends gradually, with a quicker middle section | Smooth transitions in complex mixes |
| Inverted Fade | Volume increases then decreases, or vice versa | Creating suspense or surprise in audio tracks |
| Crossfade | Overlapping of two audio tracks where one fades out as the other fades in | Transitioning between songs, blending scenes in film |
Understanding these nuances is vital to utilizing audio fades to enhance an audio piece’s storytelling and emotional impact.
Experiment with all audio fade types to get used to the different fading options!
2. Tools For Audio Fading
Analog Vs. Digital Audio Fading
The choice between analog and digital tools for audio fading is fundamental in shaping the sound quality and character of the fade.
Analog fading, traditionally done using mixing consoles, offers a warmer, more organic sound. This method is often favored in music genres that benefit from a richer, more textured audio quality. However, analog fading requires physical equipment and can be less precise than digital methods.
Digital audio fading, on the other hand, is performed using software and offers unparalleled precision and control. Modern digital audio workstations (DAWs) provide a range of fading tools and presets, allowing for meticulous adjustments down to the millisecond.
This precision makes digital fading a go-to choice for most contemporary audio editing tasks, particularly in podcast production, film sound design, and music.
Recommended Software For Effective Audio Fading
Several digital audio workstations excel in providing efficient and user-friendly fading capabilities.
Software like Adobe Audition, Pro Tools, and Logic Pro X are industry standards known for their robust editing features and seamless fade functionalities.
More straightforward and intuitive programs such as Audacity or GarageBand can be excellent starting points for beginners. These tools offer basic fading options suitable for most amateur and semi-professional needs.
When selecting software for audio fading, consider factors such as the user interface, range of fading options, compatibility with your hardware, and overall workflow efficiency. Each software has unique strengths, and choosing the right one can significantly enhance your audio editing experience.
Free Vs. Paid Audio Fading Tools
The decision between free and paid audio fading tools often depends on the user’s level of expertise and the requirements of their projects.
Free tools like Audacity offer essential fading functions and are ideal for beginners or those working on simple audio projects. These tools are a great way to learn the fundamentals of audio fading without financial investment.
Paid tools, however, provide advanced features, greater customization, and higher-quality outputs. They are typically more robust and come with professional support and regular updates.
For serious audio editors and professionals, investing in paid software like Pro Tools or Ableton Live can be worthwhile for their advanced features and long-term benefits.
3. Techniques For Seamless Audio Fades
How To Fade Audio Seamlessly: Step-By-Step Guide
Achieving a seamless audio fade is a skill that can significantly enhance the quality of any audio project. Here’s an essential step-by-step guide:
- Select The Right Fade Type:
Choose from linear, logarithmic, or exponential fades based on your project. - Determine The Fade Length:
Decide how long the fade should last. Longer fades tend to be more subtle, while shorter fades create a more abrupt change. - Adjust The Fade Curve:
In your DAW, adjust the fade curve for a more natural sound. Depending on the desired effect, this could mean a gradual start with a quicker end or vice versa. - Listen And Refine:
After applying the fade, listen to it in the context of the entire track. Adjust as necessary to ensure the transition is smooth and meets the project’s requirements.
Timing And Amplitude In Audio Fading
The timing and amplitude of an audio fade play crucial roles in its effectiveness. Timing refers to when the fade occurs and its duration, while amplitude involves the volume level changes during the fade. Getting these elements right is critical to a successful fade:
- Timing:
The fade should align perfectly with the rhythm and flow of the audio. Inappropriate timing can make a fade feel jarring or out of place. - Amplitude:
The volume changes should be smooth and consistent. Sudden drops or increases in volume can disrupt the listening experience.
Creative Audio Fades In Different Audio Formats
Fades can be used creatively in various audio formats to achieve different effects:
- Music Production:
Fades can create dramatic intros or outros or subtly transition between different song sections. - Podcasting:
Gentle fades can bring background music in and out, enhancing the narrative without overpowering the spoken word. - Film Sound Design:
Fades help blend sounds and music with the visuals, ensuring a cohesive audio-visual experience.
Experimenting with different types of fades and their application can bring a new level of sophistication to your audio projects. Understanding these techniques allows you to manipulate the listener’s experience, guiding them through the auditory journey you’ve crafted.
4. Audio Fading Mistakes And How To Avoid Them
Identifying And Correcting Common Audio Fading Errors
Even experienced audio editors can make mistakes when it comes to audio fading.
Common errors include abrupt fades that disrupt the flow of the track, fades that are too long or too short for the intended effect, and misaligned fades that don’t sync with the rhythm of the audio.
To correct audio fading errors, it’s crucial to:
- Review Fades In Context:
Always listen to your fades within the mix to ensure they fit seamlessly. - Adjust Fade Length:
If a fade feels out of place, try lengthening or shortening it to find the right balance. - Align Fades With The Audio’s Rhythm:
Make sure your fades align with the natural rhythm of the audio for a more cohesive sound.
Balancing Volume Levels In Audio Fading For Consistency
Maintaining consistent volume levels throughout a track is vital. Inconsistent volume can be distracting and give a project an unprofessional quality.
When applying fades, pay attention to the overall volume levels of your track. Use tools like normalization and compression to balance the audio and ensure that fades contribute to the track’s dynamics without causing abrupt changes in volume.
Tips For Maintaining Audio Quality During Audio Fades
Audio quality can sometimes be compromised during the fading process, especially with digital fades in compressed formats. To maintain high audio quality:
- Use High-Resolution Audio Files:
Work with the highest quality audio files possible to avoid degradation during editing. - Be Cautious With Compression:
Be mindful of the effects of compression on your audio, especially after applying fades. - Monitor For Artifacts:
Listen for any digital artifacts that might be introduced during the fading process and adjust accordingly.
Properly executed fades should enhance the audio experience without drawing attention to themselves.
By avoiding common mistakes, balancing volume levels, and prioritizing audio quality, you can ensure that your fades contribute positively to your audio projects.

5. Advanced Audio Fading Techniques
Exploring Automated Audio Fades And Audio Envelopes
Automated fades and audio envelopes represent advanced techniques that offer precision and creativity in audio editing.
Automated fades, available in most DAWs, allow for pre-programmed fade-ins and fade-outs, which are particularly useful in repetitive tasks or extended projects.
On the other hand, Audio envelopes provide a dynamic way to control volume over time, offering nuanced control for complex fading effects.
By mastering these tools, audio editors can create intricate fade patterns that would be challenging to achieve manually.
Integrating Audio Fades With Other Audio Effects
Audio fades can be combined with other effects such as reverb, delay, or EQ for enhanced sound design. For example, you are applying a reverb effect before a fade-out can create a sense of space and depth.
Similarly, adjusting the EQ during a fade can highlight or suppress specific frequencies, adding sophistication to the fade.
The key is to experiment and understand how different effects interact with each other to create the desired outcome.
Custom Audio Fading Curves For Unique Soundscapes
Customizing the curve of an audio fade can drastically change its impact on the listener. Most DAWs allow editors to tweak the fade curve, providing options beyond the standard linear, logarithmic, and exponential fades.
By adjusting these curves, editors can create unique fading effects that cater specifically to the needs of their project.
Customizing the curve allows for a high level of control and creativity, whether a sharp, sudden decrease in volume for a dramatic effect or a slow, gradual fade for a gentle transition.
Advanced audio fading techniques like these distinguish professional-grade audio work from the rest. They provide the tools to create highly polished and sophisticated audio pieces that captivate and engage the audience.
6. Practical Audio Fading Applications
Audio Fading Techniques In Music Production
Audio fades are employed in music production to create dynamic and emotional impacts. For instance, a fade-in can gradually introduce a track, building anticipation, while a fade-out can provide a natural and satisfying conclusion.
Fades are also pivotal in transitioning between different song sections, from verse to chorus, adding to the song’s narrative flow.
Furthermore, creative fading can be used within a track to highlight or diminish certain elements, like bringing a guitar solo to the forefront or softly muting background vocals.
Utilizing Audio Fades In Podcasting And Broadcasting
Podcasting and broadcasting extensively use audio fades to ensure a smooth and professional sound. Fades are crucial in managing transitions between segments, from an introduction to the main content or between different speakers.
They also significantly integrate background music and sound effects, ensuring these elements enhance rather than distract from the spoken content. Skillful fading in these mediums can substantially improve the clarity and listenability of the content.
Enhancing Video Projects With Audio Fades
In video projects, audio fades are essential for seamlessly aligning audio with visual elements. They help set the mood, emphasize vital moments, and provide smooth transitions between scenes.
For example, a gradual fade-out of music can coincide with the end of a location, signaling a shift in tone or setting. Similarly, fading in sound effects can enhance the realism of a scene without overpowering the dialogue or visuals.
Effective use of audio fades in video editing contributes significantly to the production’s overall quality and storytelling.
Each medium presents unique challenges and opportunities for audio fading, and understanding these nuances is critical to practical application.
Whether in music, podcasting, or video, skillful use of fades can significantly enhance the final product, providing a polished and professional finish.
7. Audio Fading Tips And Tricks
Insider Advice For Better Audio Fades
Seasoned audio professionals often have a trove of tips and tricks that can elevate the quality of audio fades.
One key piece of advice is always to trust your ears.
While visual aids in DAWs are helpful, ultimately, the auditory experience matters most. Editors are encouraged to listen carefully to their fades in different contexts and through various speakers or headphones to ensure they sound natural and effective.
Another tip is to utilize automation for complex projects. Automation allows for precise control over the volume levels at different points in a track, making it possible to create intricate fades that are consistent across multiple takes or sections.
Commonly Overlooked Audio Fading Techniques
Some audio fading techniques take time to be noticeable but can significantly impact the final product.
For example, using reversed fades can create unique sound effects, adding an element of surprise or novelty to a track. Additionally, experimenting with different fade lengths and shapes in unconventional ways can yield exciting results, especially in genres that thrive on innovation, like electronic or experimental music.
Remember, the key to mastering audio fades lies in experimentation, practice, and a keen ear for detail.
8. Audio Fading: Get Seamless Audio Transitions
Recap Of Key Audio Fading Techniques
Audio fading is a fundamental skill in audio editing, integral to achieving seamless transitions and a polished final product.
Basic techniques include selecting the appropriate fade type for your project, whether linear for a uniform decrease, logarithmic for a more natural tapering off, or exponential for a dramatic effect.
Understanding the context and purpose of your fade is crucial in making the right choice.
Another essential aspect is mastering the timing and amplitude of fades. This involves not just where the fade occurs but also its duration and how it affects the overall volume dynamics of the track.
Proper timing ensures that fades feel natural and enhances the flow of the audio.
Best Practices In Audio Fading
Best practices in audio fading include continuously refining your skills through training and staying updated with new software and techniques.
Always prioritize the listener’s experience, ensuring that fades complement the audio without becoming a distraction.
Use high-quality audio files to maintain sound integrity and avoid artifacts that can arise from lower-quality files or excessive compression.
Implementing Audio Fading In Your Projects
Implementing audio fading effectively requires a blend of technical knowledge and creativity. Feel free to experiment with different fading techniques and applications.
Whether you’re working on music, podcasts, or audio for video, thoughtful and well-executed fades can significantly enhance your project.
Though an essential skill, audio fading is vital for creating professional-quality audio. With practice and attention to detail, it can become an invaluable tool in your audio editing arsenal.
Happy fading!
9. FAQ
- How To Choose The Right Audio Fade For Your Project?
The proper fade depends on the project’s context and desired effect. Use linear fades for uniform volume decreases, logarithmic for natural endings, and exponential fades for dramatic results. Consider your audio’s genre, mood, and pacing when selecting a fade type.
- Can You Automate Fades In Most Audio Editing Software?
Yes, most modern digital audio workstations (DAWs) allow for automation of fades. This feature enables precise control and consistency, which is especially useful in complex projects or when dealing with multiple tracks.
- What Are The Biggest Challenges In Mastering Audio Fades?
Mastering audio fades involves understanding the subtle timing, amplitude, and context nuances. The challenge lies in using fades as a technical tool and a creative element that enhances the overall listening experience.
- How Do Different Audio Fade Shapes Affect The Final Sound?
Different fade shapes can create various emotional and auditory effects. For instance, linear fades provide a steady decrease in volume, making a sense of uniformity. In contrast, logarithmic fades can give a more natural, gradual conclusion, and exponential fades create a sense of urgency or abruptness.
- Is It Possible To Fade Multiple Audio Tracks Simultaneously?
Yes, it’s possible to fade multiple tracks simultaneously in most DAWs. This technique helps create cohesive transitions in complex projects, ensuring all mixed elements blend smoothly.